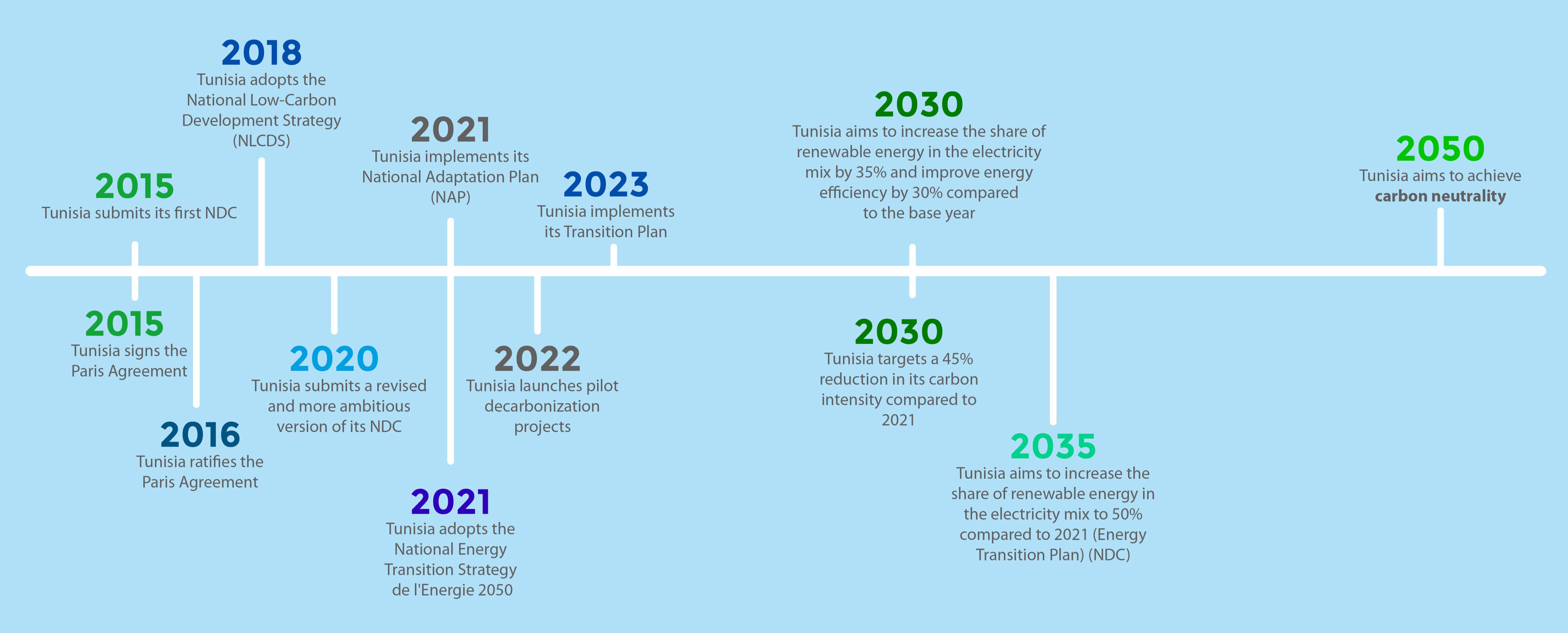
The Paris Agreement, adopted at COP21 in Paris on December 12, 2015, aims to accelerate global efforts to combat climate change. It commits all parties to transition towards a low-carbon economy, in order to limit global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursue efforts to limit it ideally to 1.5°C.
Tunisia has engaged to reduce its carbon intensity by 45% by 2030 compared to 2010. This ambitious plan includes initiatives to strengthen climate resilience and adopt a sustainable and inclusive development model.
Implementing this strategy will require significant financial resources, estimated at around USD 19.4 billion between 2021 and 2030
To support these efforts, the National Agency for Energy Conservation (ANME) has developed the DecarboACT digital platform to facilitate access to information and encourage businesses to embrace the energy transition.
Given the carbon emission factor of the electricity sector (97% from natural gas) and the limited use of clean energy in the supply chain (transportation, thermal utilities, etc.), Tunisian companies are requested upon to make an additional effort.
Tunisia has demonstrated a clear commitment and political engagement, as evidenced by a suitable institutional framework, a coherent legal framework, and financing mechanisms backed by the Energy Transition Fund, ensuring the sustainability of actions and programming.
Tunisian companies contribute to:
In parallel, Tunisia has established a conducive legal and incentive framework to foster energy efficiency and renewable energy, offering a comprehensive range of services, equipment, and financing solutions to accelerate a cost-effective low-carbon transition.
Additionally, Tunisia is committed to supporting Tunisian exporters in meeting international requirements, particularly those related to transparency through carbon accounting.